The benefits and challenges of enterprise 360 views
Andres Baquero – May 12th, 2021

Many organizations continue to adopt the 360-degree view of the customer concept as part of digital transformation. As if the latter wasn’t complex enough, trying to capture the moving target that is the modern customer is a tricky task as they move between various digital channels.
Knowing more about customers, partners, employees or prospects provides business value that drives strategy and decision making. Understanding where any customers are digitally and what motivates them to perform well or purchase, change providers or respond to marketing will have a major impact. But, collecting and analyzing that data poses fresh challenges.
Defining the 360-degree customer view?
A 360-degree view is a holistic profile of an entity (e.g., a customer, employee, citizen, donor, constituent, etc.) that that captures data from across channels and systems, aggregates it at the individual level to understand what is important and applies insights to deliver personalized and engaging experiences as well as achieve organization performance objectives.
The aim of a 360-degree view is to gather every available insight of a customer’s data in one place. That can mix internal basics like legacy contact information, sales, donations or transactional history and service engagement to external interactions on social media or enterprise platforms.
The goal is to take that information and aggregate it at the individual level to extract key insights and understanding for marketing, sales, analytics or other efforts. Using analytics, firms can apply those insights to deliver personalized and engaging experiences, and help meet internal performance objectives.
The benefits of a 360-degree view
The goal for most organizations is the ability to quickly assess a changing or evolving situation and respond appropriately to improve business results. Putting all their information in one place speeds up records findability and business processes, while the combined 360-degree view creates better data to base decisions on.
Business intelligence in the era of predictive analytics, provides the ability to forecast client behavior and predict future actions. These help drive predictive scoring models, personalization of campaigns and other goals, all with greater accuracy and flexibility, improving business operations.
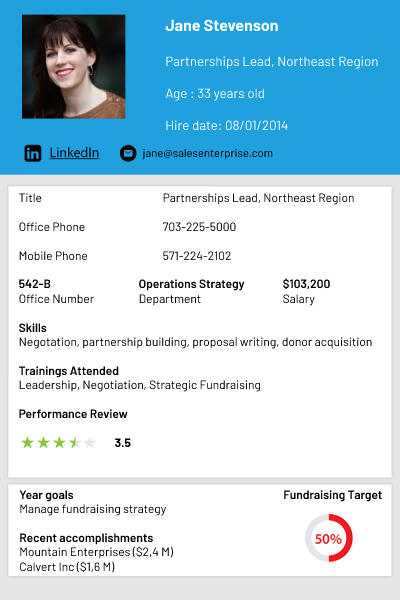
Consider a non-profit where the firm wants a dashboard view of what campaigns work best and where the majority of donors engage, or stop donating. Or, for employees, an end-to-end picture of the employee’s journey and experience within the organization is key to retention, reward and hiring practices. 360 employee views are becoming even more relevant as the emerging work-from-anywhere economy adds new complexity to building journeys and finding information.
Technology platforms that deliver 360-degree views
|
Traditional business intelligence and analytic tools often operated in silos. Building a 360 view typically requires the use of one or more of these platforms to deliver a single view:
|
Recently, SAS software providers offered advanced technologies to provide a stronger user experience for 360 views using ‘hover cards’ that run on browsers as an immediate visual representation of client’s interactions from multiple systems.
The challenges in achieving a 360-degree view
As with many analytics projects, the key challenge with building 360 views comes from classifying and bringing together data from disparate sources. From CRMs, transactional data, employee or donations data to other legacy systems, they can prove hard to integrate.
Further challenges include:
- Large amounts of data on legacy systems, migrating legacy data to the cloud may require expensive custom integrations.
- No digital trace footprint for many interactions or they are not replicated back to a central warehouse.
- Data is not properly categorized, is unstructured or where elements have changed over time (like id codes) can add complexity to migration tasks.
- Taxonomies across legacy and more current systems differ or data quality is not optimal.
- The size of historical datasets and the speed at which data continues to grow means categorization and cleanup are too great for manual editing. However, data profiling and categorization tools for structured and unstructured data have come a long way to support this process.
- Central data warehouses are not always available due to organizations’ budget or policies on data accessibility and security, while high data volume amounts created on a regular basis, mean that data is not always accessible.
- Many organizations find it challenging or expensive to fully migrate to the cloud and retire legacy systems. As data is the fuel for more complex processes such as scoring, they can only be achieved, if continuously updated and maintained by automated backends.
Up next, Strategies for Effectively Implementing 360 Views.
If you want to find out how your organization can benefit from 360 views, CRM and advanced analytics services, you can contact us.
